🌍 Introduction: What is CFR?
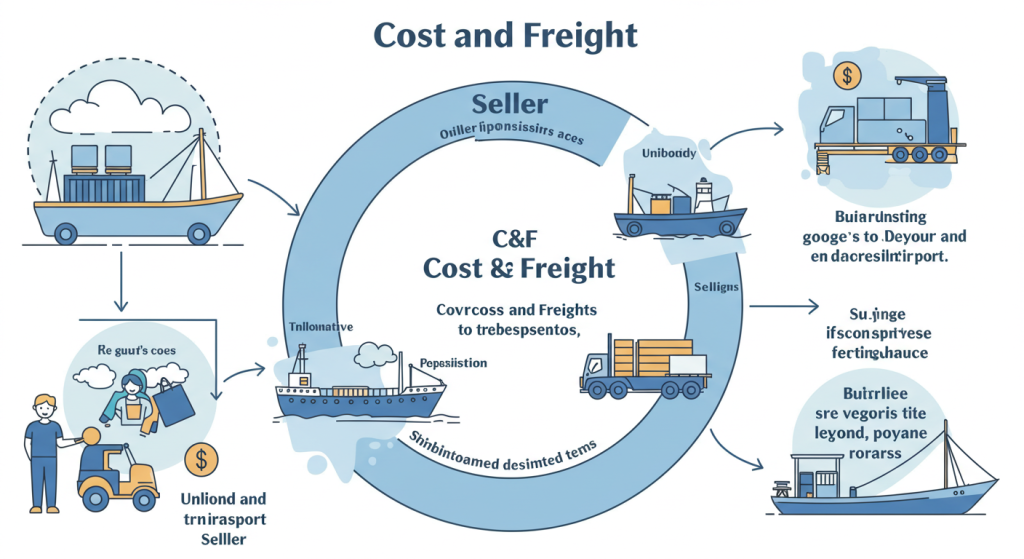
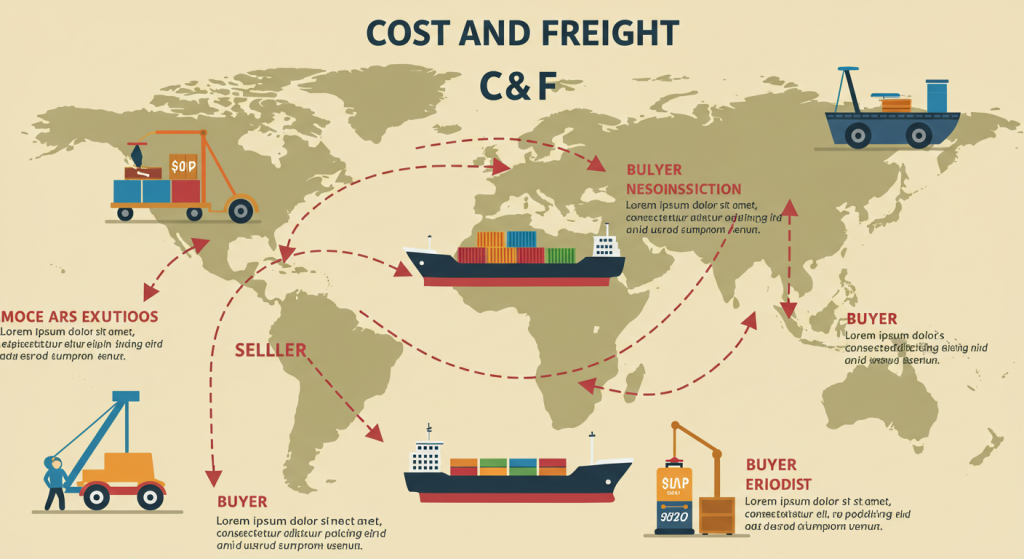
CFR, or Cost and Freight, is one of the Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) that determines the responsibilities of the buyer and seller in international trade. It specifies that the seller is responsible for covering the costs and freight charges to transport goods to a designated port of destination. However, the risk of loss or damage to the goods is transferred to the buyer as soon as the goods are loaded onto the vessel at the port of shipment.
💰 Seller’s Responsibilities Under CFR
The seller’s obligations under CFR include the following:
- Transport Costs: 🚢
The seller is responsible for paying the costs of transporting goods to the destination port. This includes freight charges for shipping the goods by sea, rail, or land, depending on the agreed mode of transport. - Export Duties: 📜
The seller must handle all the necessary export duties and clearances, ensuring that the goods comply with export regulations in the country of origin. - Freight Insurance (Optional): 🛡️
While the seller is not required to provide insurance for the goods during the voyage, they may choose to do so at their discretion.
🌟 Buyer’s Responsibilities Under CFR
Once the goods are loaded onto the vessel, the buyer assumes responsibility for the following:
- Risk of Loss or Damage: ⚠️
The buyer takes on the risk of loss or damage to the goods as soon as the goods are loaded onto the vessel. This is why it is crucial for the buyer to arrange for marine insurance to protect the goods during transit. - Import Duties and Customs Clearance: 📦
Upon arrival at the destination port, the buyer is responsible for paying any import duties and handling customs clearance. - Cost of Discharge: 💵
The buyer must pay for the unloading of the goods once they arrive at the port of destination.
🌐 Advantages of Using CFR in International Trade
- Cost Transparency: 💡
CFR provides clear understanding of the costs involved in shipping, making it easier for both parties to agree on terms. - Control Over Shipping: ⛴️
The seller controls the freight arrangements, allowing them to choose reliable shipping lines and negotiate freight rates. - Shared Responsibility: 🤝
With CFR, the seller and buyer share responsibilities, with the seller handling transportation costs and the buyer taking over after the goods are loaded.
⚖️ Disadvantages of CFR in International Trade
- Risk Transfer: ⚠️
Even though the seller handles the shipping costs, the buyer assumes all risk once the goods are loaded onto the vessel. This can be risky if proper insurance is not arranged. - Import Delays: ⏳
As the buyer is responsible for customs clearance, any delays in the import process at the destination port may affect the timely delivery of the goods.
📦 Conclusion: When to Use CFR in International Trade
CFR is a commonly used Incoterm for sea freight where both the seller and buyer share certain responsibilities. While the seller manages the transportation and freight costs, the buyer should be aware of the risks associated with receiving the goods once they are loaded onto the ship. It is crucial to ensure that both parties understand their responsibilities to avoid any disputes or complications during the shipping process.